8. Maritime spaces

NANO-ck
Mise-à-jour le 25 March 2024, 2 minutes de lecture
Maritime spaces
Importance of maritime spaces
- Ressources : Energy, raw materials, food
- Trade : Transport of goods, migration, communication cables
- Environment : Climate change and biodiversity
- Power : Hard power, contested EEZs Choke points
Geographical Factors leading to unequal globalization
- Factors aiding globalization
- Natural harbours
- Investment in transport and communication infrastructure
- Major ports, 600 million container movements each year
- Factors disadvantaging countries
- Landlocked countries
- Remote islands
- Climate
- Ressources
- Intensifiers : Countries with a lot of ressources become wealthy, if they have a good government
- With a bad government, only the elite has access to these ressources
- Intensifiers : Countries with a lot of ressources become wealthy, if they have a good government
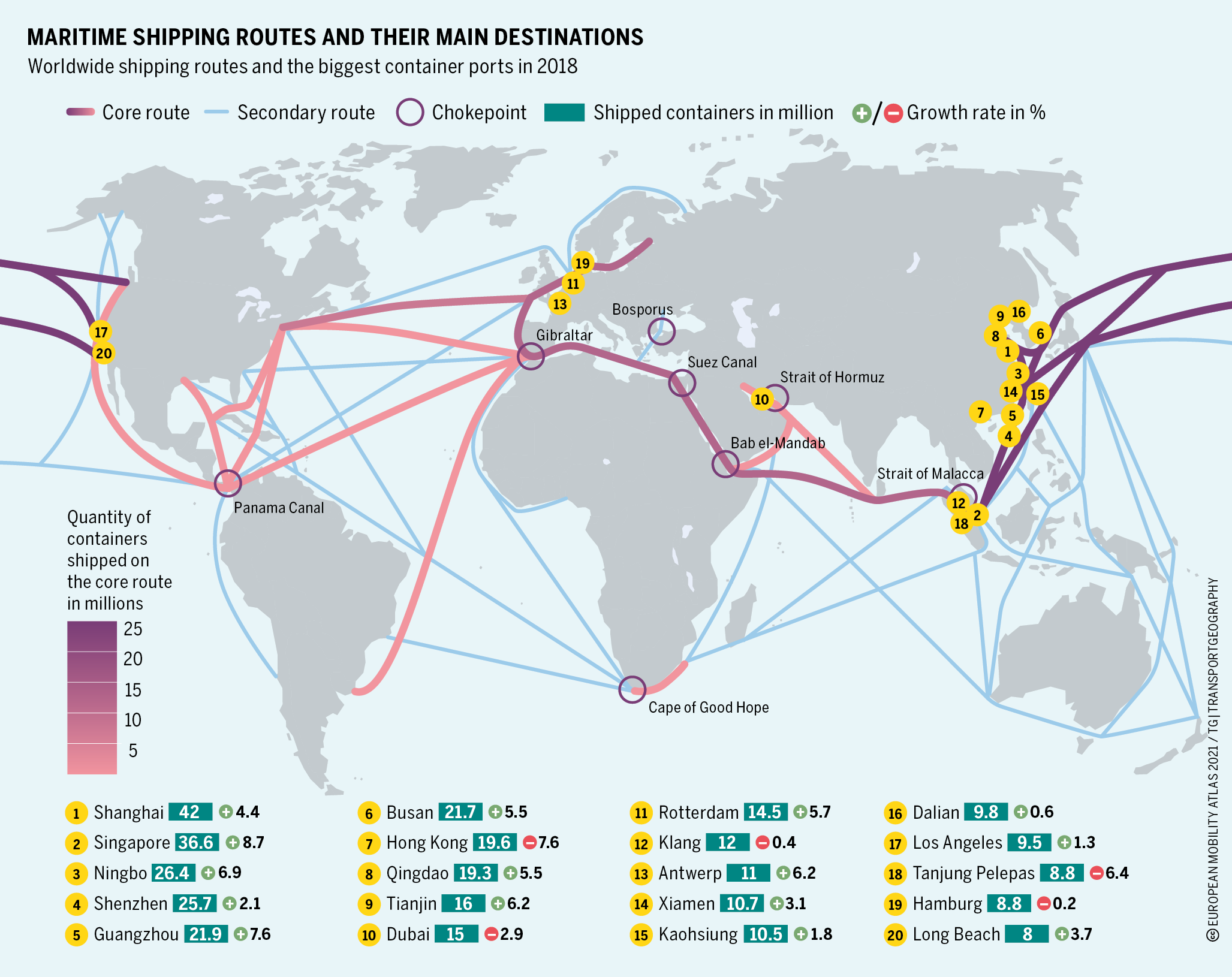
Submarine cables and hubs
- More the 1 million Kms of undersea flexible cables
- Issues with lands refusing those cables and spying
"Two thirds of cable failures are caused by accidental human activities, fishing nets, and trawling, also
Energy ressources
Why the Suez Canal and other choke-points face growing pressure.
- Gas pipes can also go under the sea
- Gas pipes explosions
A few damages
- Undersea telecom cable connecting Estonia and Sweden damaged
- Affected at same time as connecting gas pipeline damaged
- Retribution after the country requested to join NATO?
Fishing
- A third of fishing is illegal
- A third of fish stocks are overfished
Role of the state and MNOs
- States need to secure things like energy
- Securing safe routes
- Exploitation of offshore resources
- Secure communication cables
- Protection of maritime ecosystems
- Reducing climate change impacts
- EEZs give rights to fishing, building, infrastructure and natural resources
- Fishing disputes in 1970s
- 1982 UNCLOS (United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea) amended in 1994
Contested EEZs boundaries
- Mainly issues with the Philippines and China
- France has the second largest EEZ after the US
Case study : The Arctic
- Climate change impacts
- New routes ? Economic impact ?
- Increased fishing due to warmer waters ?
- Transport infrastructures lack
- Shipping movements in an ice free Arctic
- Summer sea ice is shrinking by 12-13% a decade
- Ice Breakers save the Arctic’s connection to the rest of the world
Who controls the Arctic ?
- Russia owns 53% of the Arctic coastline
- Since 2007 at least 50 Soviet-era military outposts have been reopened
- The Arctic route has drawbacks
- Assurance fees
- Navigation season of three to four months each year
- Unpredictable ice conditions
Strategies
- Legal: Unclos
- Political: Diplomacy individually within ASEAN MNO
- Military US Military exercises may be 16 weeks
Disponibilité & Aide
Ce site est à la disposition de tous, pour consulter et participer à la prise de notes.
Garantie
Aucun contenu n'est garanti, et ne peut être utilisé comme référence fiable.